Life Changing Breathing.
The Revolutionary Magnetic Nasal Strip
Excellent 4.5 | 1,000,000+ Customers
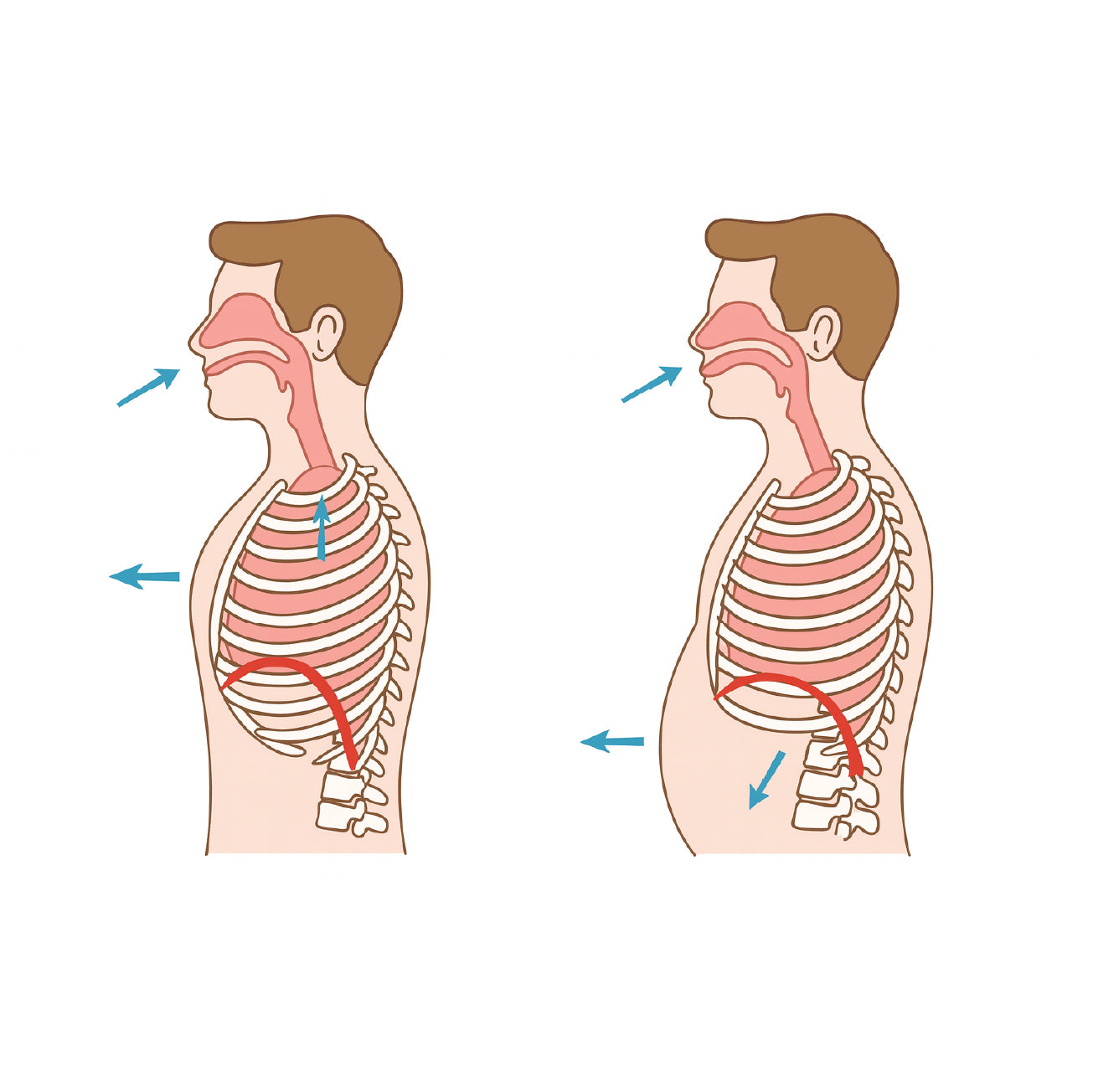
4 out of 5 people are airflow limited. Are YOU one of them?

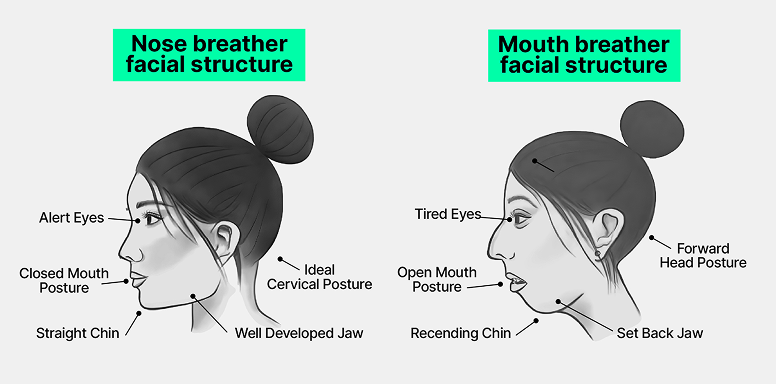
How Limited Airflow Effects Your Health
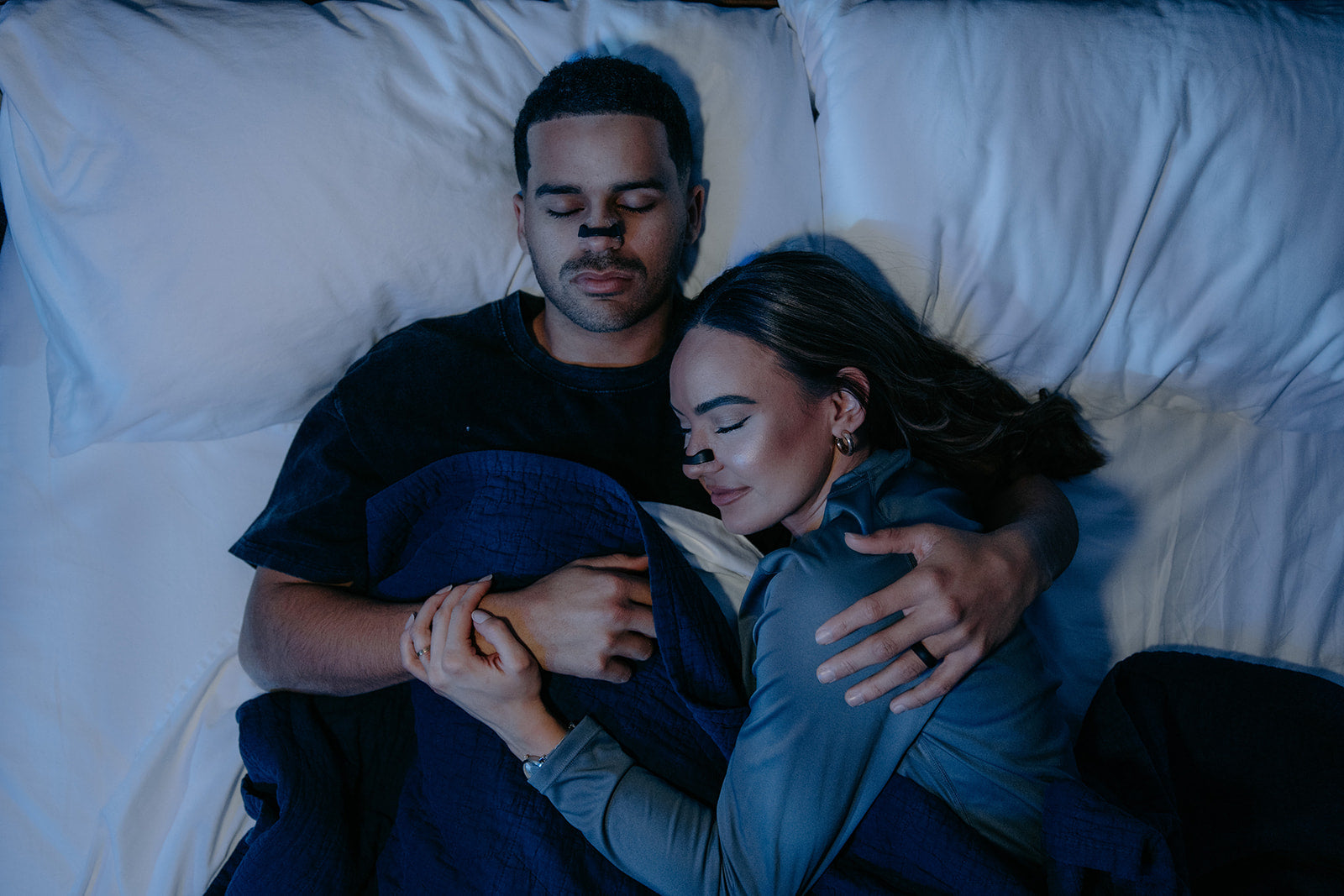

Introducing Intake Breathing.
Trusted by Millions. Backed By Research. SleepScore Labs confirms what our users experience every day, better breathing and better sleep.
-
0%Reduction in Snoring*
-
0%Relief From Sinus Pressure*
-
0%Deeper & More Restful Sleep*
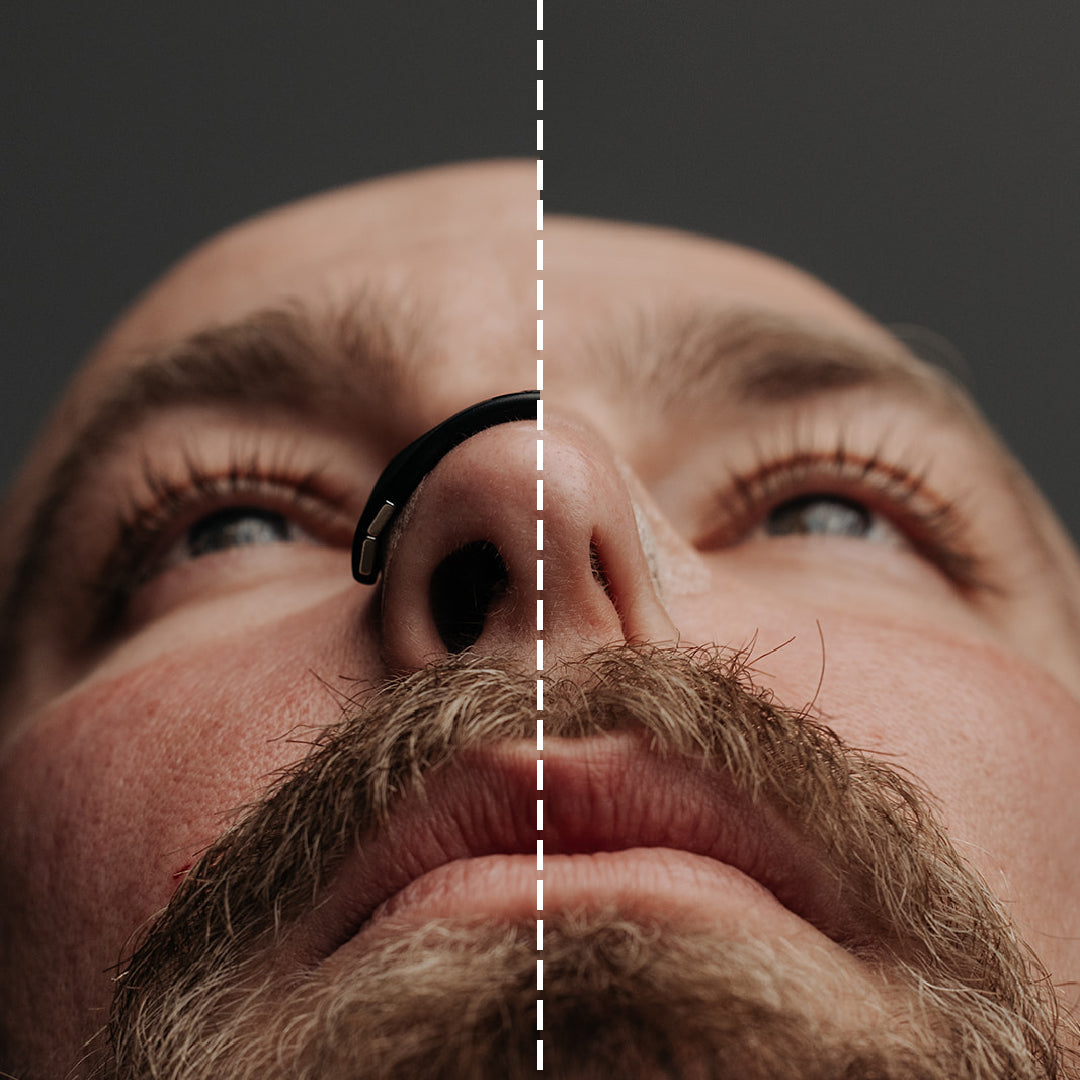
What Sets Us Apart
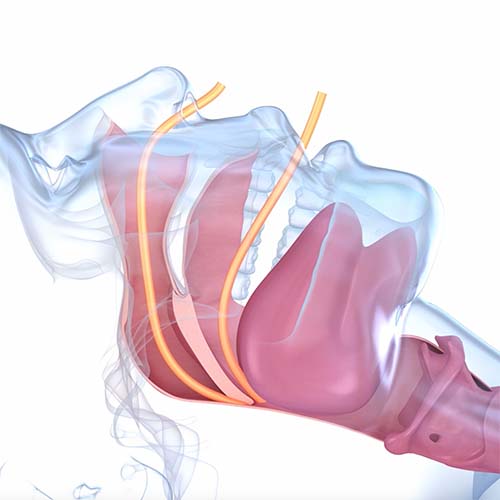
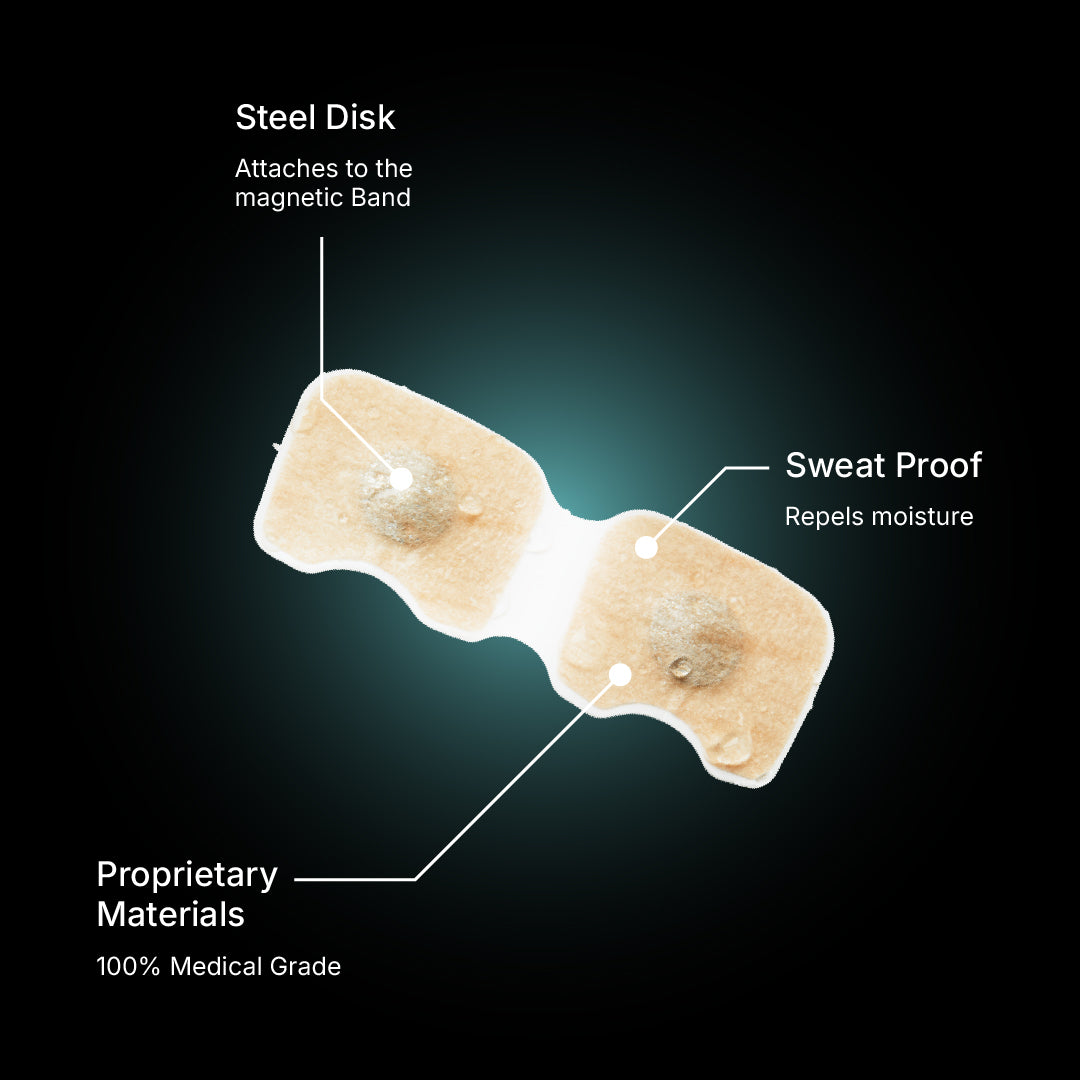
Intake opens your airways wider, stays put when strips slip, wicks sweat, and won’t collapse when you breathe in.
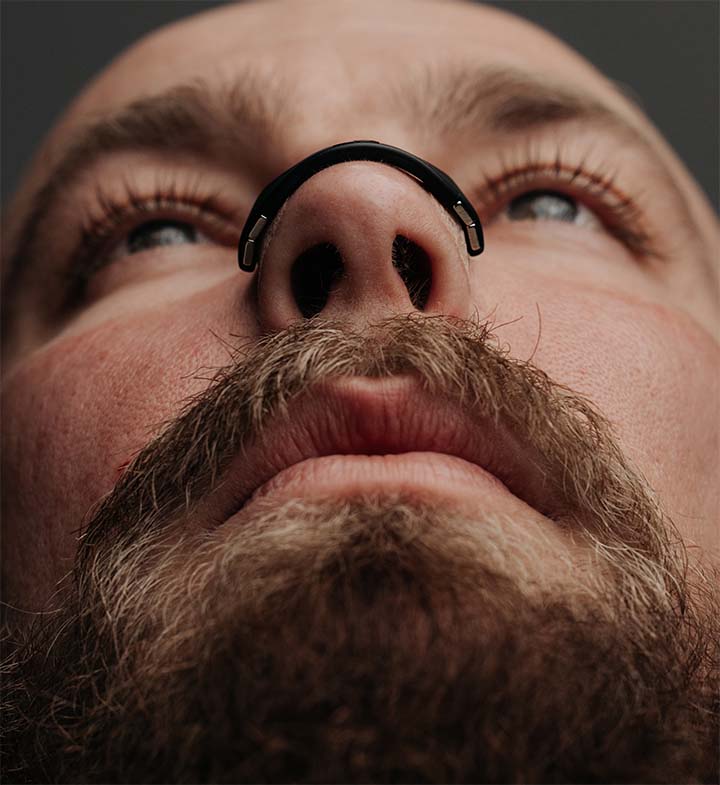
Intake
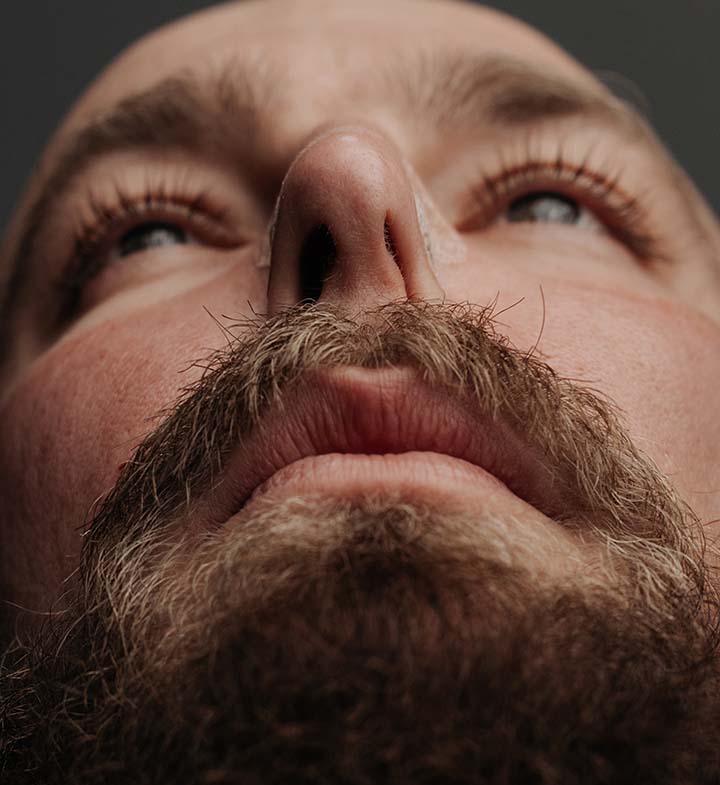

Nasal Strip
How To Use Intake
+1,000,000 Customers
FAQ
Will the tabs actually stay on overnight or when I’m sweaty?
Yes. Intake was originally designed for motocross and high-intensity athletic sports, where sweat, movement, and helmets make adhesion tough. The tabs are built to handle those conditions—and they can also stay on reliably through a full night’s sleep.
For best results:
- Apply to clean, dry skin (no lotions, sunscreen, or makeup).
- Wipe the area with a little alcohol or wash and fully dry.
- Press the tabs firmly in for 10–15 seconds.
With correct placement, the tabs stay secure during workouts, runs, and even all-night wear.
Will this make my nose permanently bigger?
No. Intake is an external nasal dilator. It temporarily supports the nasal valve to improve airflow while worn and your nose returns to baseline when removed. Only surgery or trauma can permanently change nasal soft tissue or cartilage.
I have sensitive skin. Is the adhesive safe?
Yes. Intake pads are made with USA-made, medical-grade materials that are designed to be safe for skin contact. The adhesive is latex-free and hypoallergenic.
Will it hurt or feel uncomfortable?
No—Unlike nasal strips that pull on the bridge of your nose, Intake works differently:
- External only: Nothing goes inside your nose. The band and pads sit gently on the outside, so there’s no internal irritation.
- No bridge pressure: Because it anchors to the sidewalls of your nose, you don’t get that tugging or pulling across the bridge that many strips cause.
- Customizable fit: Intake comes in different sizes, and you can choose how wide you want to open your nose. That means you control both the airflow and the comfort level.